What is Ammonium Bisulfite?
Before diving into its intricacies, let's understand the essence of ABS. It's an inorganic compound formed by the reaction of Ammonia and Sulfurous Acid. This seemingly simple compound, which is also known as Ammonium Hydrogen Sulfite, acts as a potent oxygen scavenger, a reducing agent, and an effective preservative, making it a highly sought-
after chemical for various applications across a wide range of industries.
Ammonium Bisulfite Chemical Composition
Ammonium bisulfite is a fascinating inorganic compound exhibiting unique structural and functional properties. Its molecular composition reveals a central sulfur atom bound to three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement.
ABS exists as colorless crystals when dry and as a clear and colorless solution when dissolved in water. It has a pungent, sulfurous odor and is relatively unstable and decomposes over time, releasing sulfur dioxide gas. Its properties can be categorized as follows:
Physical: White, crystalline solid, slightly acidic pH (~5.0), soluble in water.
Chemical: Oxygen scavenger, reducing agent, preservative.
Thermal: Melting point: 107°C, decomposes at higher temperatures.
Safety: Generally considered safe, but can cause skin and eye irritation.
What is the Chemical Formula of Ammonium Bisulfite?
The chemical formula for Ammonium bisulfite is NH₄HSO₃. It's important to note that it's written with the subscript for Ammonium (NH₄) and not just N and the subscript for HSO₃ as a single unit, not H2SO3. This emphasizes that the compound exists as a salt-like structure with Ammonium cations (NH₄+) and bisulfite anions (HSO₃-).
(NH4)HSO4
What is the Structure of Ammonium Bisulfite?
The structure of Ammonium bisulfite can be described in two ways:
Lewis Structure:
In the Lewis structure, all atoms are represented by their element symbol surrounded by dots representing their valence electrons. Here's how it looks for Ammonium bisulfite:
H H H
| | |
H-N+---H---O=S-O-H
| |
H H
The central nitrogen atom bears a positive charge (N+) and forms single bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
The sulfur atom is double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to another oxygen atom with a hydrogen atom attached.
The single and double bonds account for the eight valence electrons around each atom, except for the positively charged nitrogen which has only seven.
Ball-and-Stick Model:
The ball-and-stick model represents atoms as spheres connected by sticks representing bonds. Here's the ball-and-stick model for Ammonium bisulfite:
H H H
/ | \
H--N+--H--O--S=O--H
\ | /
H H
This model emphasizes the spatial arrangement of atoms, showing the tetrahedral geometry around the nitrogen atom and the bent geometry around the sulfur atom.
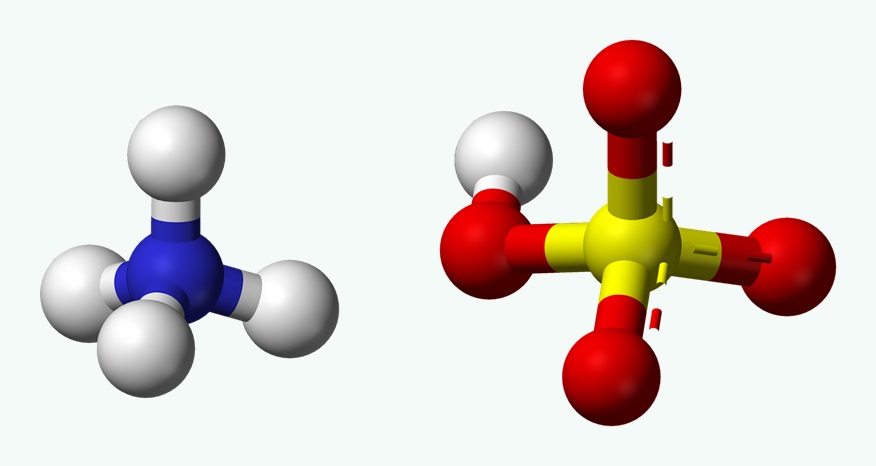
Ammonium Bisulfite Molecule, image source
Ammonium Bisulfite Uses
The true strength of ABS lies in its adaptability; from safeguarding the environment to enhancing industrial processes, it plays a pivotal role in diverse sectors.
What is Ammonium Bisulfate used for?
Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD): ABS shines as a cost-effective oxygen scavenger in FGD systems. Its ability to capture and prevent the re-oxidation of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions (back into its harmful gaseous form) in power plants and other industrial facilities significantly reduces air pollution, contributing to cleaner air and healthier communities.
Pulp and Paper Industry: ABS is a sustainable alternative to chlorine-based bleaching agents in the papermaking industry. It effectively brightens wood pulp while minimizing the harmful effects of chlorine-based bleach thus leading to a greener paper production process.
Textile Industry: In textile processing, Ammonium Bisulfite serves as a potent reducing agent. It removes unwanted coloring agents and enhances the dyeing process, ensuring vibrant fabric colors, superior color retention and fabric quality.
Water Treatment: ABS effectively neutralizes chlorine residuals and removes heavy metals like copper and zinc from water. This translates to cleaner, safer water for diverse purposes, from drinking water to industrial use.
Food and Beverage Industry: ABS acts as an antioxidant and preservative in the food and beverage industry. It helps inhibit microbial growth and prevent browning reactions thus extending the shelf life of products while maintaining their freshness and quality.
Photography: Ammonium Bisulfate acts as a fixing agent in traditional photography. It removes unexposed silver halide crystals from photographic film, making the image permanent.
Other Applications: The applications of ABS goes beyond the above mentioned scope, finding its way into metal surface treatment, leather processing, rubber production, and fire retardant formulations.
Advantages of Using Ammonium Bisulfite
The allure of ABS goes beyond its diverse applications. It boasts a set of distinct advantages that make it a compelling choice for various industries:
Cost-Effective: Compared to other chemical solutions, ABS enjoys a relatively lower price point making it a financially viable choice for businesses of all sizes.
Environmentally Friendly: In an age of environmental consciousness, Ammonium Bisulfite stands out as a greener alternative to its chlorine-based counterparts. Its sulfur-based chemistry minimizes toxicity and ecological footprint.
Safe and Easy to Handle: ABS is generally considered a safe chemical with minimal health hazards when handled responsibly. Its water solubility and relatively mild nature make it easier to handle and transport compared to other harsh chemicals.
Efficient and Effective: From efficient FGD to sustainable pulp bleaching, Ammonium Bisulfite has been a dependable choice for achieving consistent results.
Ammonium Bisulfite Physical States
ABS can be used in both solid and liquid forms, each with its own properties and applications. The rule of thumb is that for strength, stability, and design flexibility industries choose the solid form. But for ease of application, detail, and thin-walled parts, the solution is the favorite alternative.
When in solid state, this thermoplastic polymer comes in pellets, granules, sheets, or filaments. It is strong and durable and can be easily machined, drilled, and formed.
As a solid, it is mainly used for injection molding for various parts and components like Lego bricks, car parts, and appliance housings, extrusion for profiles, pipes, and sheets, as well as 3D printing with filament extrusion.
What is the Use of Ammonium Bisulfite Solution?
Ammonium Bisulfite Solution is a liquid mixture of ABS polymer dissolved in a solvent (usually acetone or methyl ethyl ketone). Compared to its solid form, it has lower viscosity, making it easier to apply and flow into intricate shapes. It has a relatively faster drying time and is more prone to shrinkage and warping during drying.
Ammonium Bisulfite Solution is used for:
Adhesive bonding for joining ABS parts
Coating for protecting and decorating surfaces
Dipping for creating thin, uniform coatings
Impregnation for strengthening porous materials
What is the HS Code for Ammonium Bisulfite Solution?
The Harmonized System Code for Ammonium bisulfite solution is 28322090.
Impact and the Future of Ammonium Bisulfite
As industries around the world strive towards sustainability and cleaner processes while reducing production costs, the potential of ABS is expected to blossom even further. Ammonium Bisulfite’s versatility and proven advantages to its alternatives have made it a promising chemical with immense potential. In the meantime the ongoing research into new applications of ABS only further solidifies its potential as a key ingredient in shaping a greener future.
Ammonium Bisulfite Production Process
There are several methods for producing Ammonium bisulfite, each coming with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the more frequently used methods:
Absorption Process: This is the most common and straightforward method. Sulfur dioxide gas is bubbled through a solution of Ammonia, where it reacts to form Ammonium bisulfite. This process is relatively simple and requires minimal equipment. However, it can be energy-intensive and generate large amounts of waste heat.
Reaction with Ammonium Sulfite: This method which is less common than the absorption process involves reacting Ammonia with Ammonium sulfite (NH₄)₂SO₃ to produce Ammonium bisulfite. This reaction is typically carried out in a stirred reactor at moderate temperatures. It requires less equipment and is less sensitive to impurities in the reactants. However, it requires additional processing to separate the Ammonium bisulfite from the reaction mixture.
Thermal Decomposition: In this method Ammonium sulfite is thermally decomposed to produce Ammonium bisulfite and water. This process requires high temperatures and thus can be energy-intensive. But the final product is high-purity Ammonium bisulfite.
Electrochemical Production: Several electrochemical processes can also be used to produce Ammonium bisulfite, such as the electrolysis of a solution of Ammonium sulfate with sulfur dioxide. These methods can be more energy-efficient and controllably produce a high-purity product. However, they require specialized equipment and may be more costly and complex to implement.
Ultimately, the best production process for Ammonium bisulfite depends on the specific needs and constraints of the application and producer. This also depends on the desired purity and concentration of the final product.
Who are the Largest Manufacturers of Ammonium Bisulfite?
Identifying the largest manufacturers of Ammonium bisulfite can be challenging due to various factors. However, based on industry reports and available information, here are some notable manufacturers of Ammonium bisulfite:
Jay Dinesh Chemicals is an Indian conglomerate which manufactures a wide range of industrial chemicals for various industries including oilfield, food, leather, textile, metal finishing and pharmaceutical raw materials.
Dongying City Dayong Petroleum Additives Co.,Ltd. is a chinese chemical enterprise which produces drilling materials, production chemicals and water treatment chemicals.
Ammonium Bisulfite Price
The price of Ammonium bisulfite can vary depending on several factors, including the grade and purity of the final product. Industrial-grade Ammonium bisulfite is generally cheaper than food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade material. Prices may also differ based on regional availability and transportation costs.
Therefore, it's difficult to provide a single, definitive price for Ammonium bisulfite. However, to get the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information, we recommend contacting TEAMChem directly. We can provide you with specific quotes based on your specific needs and requirements.
Needless to say, If you require large quantities for industrial applications you can ask TEAMChem as your supplier in Iran about the Ammonium bisulfite price per ton (or tonne in case you prefer metrics). Should you require smaller amounts for laboratory or research purposesIf do not hesitate to inquire about the Ammonium bisulfite price per kg (kilogram). And even if you need to know the latest prices in a specific location, like in India, simply ask us about the Ammonium bisulfite price in India. As easy as that!
TEAM Chemicals: Ammonium Bisulfite Supplier in Iran
At TEAMChem, we understand the power of Ammonium bisulfite and its immense potential across various industries. We offer high-quality ABS solutions backed by expert technical support and dedicated customer service. We believe in collaborating with our customers to explore innovative applications and unlock the full potential of this remarkable chemical.