Triethylene Glycol (TEG): A Multifaceted Tool in Pharmaceutical Development
Imagine your stomach starts to act up right in the middle of an important meeting. But there is little anyone can do since even the best pills take hours to dissolve in the body. Or, suppose you are just about to step on stage for that big presentation and a wave of dry coughs hits you, stealing your breath. You fumble for your cough syrup, but the second you open it, the medicine evaporates, leaving only a faint, medicinal smell. But hold on, stop imagining for a second!
Thankfully these frustrating scenarios almost never happen in the real world, thanks to ingredients like Triethylene Glycol (TEG).
Understanding Triethylene Glycol: A Primer
Triethylene glycol (TEG) is an organic compound classified as a diol, a subset of alcohols. It belongs to the polyethylene glycol family, which gets progressively more viscous with increasing molecular weight. TEG has the chemical formula C6H14O4.
Under the Microscope: The Chemical Structure
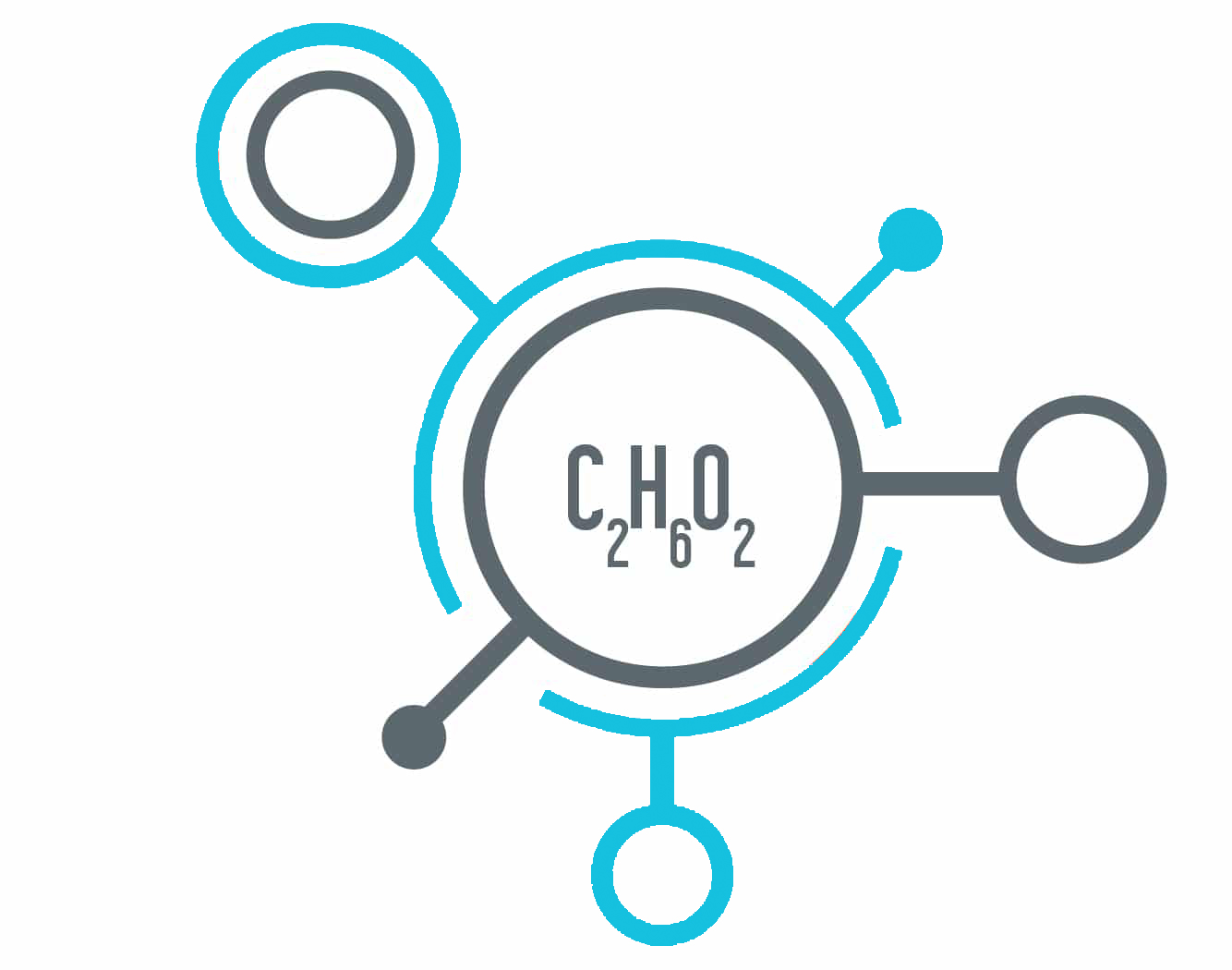
TEG consists of a chain of three ethylene oxide units (-CH2CH2O-) linked together, with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached at each end. This specific structure gives TEG its unique and quite useful properties.
Properties of Triethylene Glycol (TEG) Relevant to Pharmaceuticals
Triethylene glycol possesses unique properties that make it an incredibly valuable asset in the pharmaceutical industry. Here are some of these useful properties:
Hygroscopicity (Ability to Absorb Moisture): TEG's powerful moisture-absorbing capability helps stabilize pharmaceuticals that are sensitive to moisture degradation. It acts as a desiccant, preventing unwanted chemical reactions and prolonging shelf life.
Solubility (Miscibility with Many Solvents): TEG's ability to dissolve a wide range of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is crucial. It enhances bioavailability by ensuring that the API remains dissolved, allowing for better absorption within the body.
Viscosity (Moderately Viscous): TEG's viscosity makes it ideal for modifying the consistency and flow of pharmaceutical formulations. It can thicken liquids, such as in syrups and gels, improving ease of administration and patient comfort.
Low Volatility (Does Not Evaporate Readily): TEG extends the shelf-life of medications by minimizing evaporation losses. This is particularly important for liquid formulations where maintaining consistent dosage concentration is vital.
Low Toxicity (Relatively Safe): When used within approved regulatory limits, TEG is considered safe for pharmaceutical applications. This allows for its incorporation into various formulations without excessive safety concerns.
Partnership Potential: Companies like TEAMChem specialize in sourcing TEG alongside a wide range of other chemicals essential to the pharmaceutical industry.
Applications of Triethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Formulations
Triethylene glycol is a valuable component in various types of medications. Here's a list of its key roles in pharmaceutical formulations:
Solvents and Cosolvents: TEG's ability to dissolve many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) makes it an excellent solvent or cosolvent in liquid medications like solutions, syrups, and suspensions. This ensures the API is evenly distributed and readily absorbed by the body.
Humectant: TEG's hygroscopic nature makes it a common humectant in topical formulations like creams, gels, and ointments. It helps retain moisture, preventing these medications from drying out and ensuring optimal consistency for application and efficacy.
Plasticizer: In film coatings for tablets and capsules, TEG acts as a plasticizer, adding flexibility and reducing the risk of cracking or brittleness. This improves ease of swallowing and protects the medication.
Viscosity Enhancer: TEG's moderately viscous nature helps modify the texture and flow of liquid formulations like syrups and suspensions. It enhances their stability, palatability, and overall ease of use.
Disinfectant: In low concentrations, TEG exhibits mild antimicrobial properties, making it useful in sanitation and certain pharmaceutical preparations.
Expertise Matters: When formulating with TEG, partnering with a reliable chemical supplier like TEAMChem ensures access to high-quality TEG and the technical knowledge to ensure its effective use.
Triethylene Glycol in Drug Formulation: Solubility and Stability
Beyond its general applications, TEG plays a crucial role in addressing two fundamental challenges in drug formulation:
Enhancing Drug Solubility: Many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are poorly soluble in water, which can significantly hinder their absorption and effectiveness in the body. TEG's broad solubility profile often helps dissolve these stubborn APIs, particularly in liquid medications. By improving solubility, TEG ensures patients receive the intended dosage of the active ingredient.
Maintaining Drug Stability: Moisture, temperature fluctuations, and other factors can degrade APIs over time, reducing drug potency. TEG's hygroscopicity helps control moisture levels within medications, especially in moisture-sensitive formulations. This helps to protect the API from degradation, ensuring the medication maintains its effectiveness throughout its shelf-life.
The Role of Triethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Excipients
Excipients are inactive ingredients that serve as carriers, bulking agents, binders, and more within medications. While they don't directly treat conditions, they play a vital role in the effective delivery of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). TEG functions as a valuable excipient or supports the functions of other excipients in the following ways:
Binder: In tablet formulations, TEG can help bind excipients and the API together, ensuring the tablet's integrity and preventing disintegration before use.
Film-coating agent: TEG contributes to film coatings, improving tablet palatability, protecting the API, and potentially modifying drug release patterns.
Disintegrant Aid: When included with disintegrants (excipients that help tablets break down in the body), TEG can promote faster disintegration for rapid drug release and absorption.
Lubricant: In manufacturing processes, TEG can act as a lubricant, reducing friction and improving the flow of powders during tablet or capsule production.
Beyond Supply: Companies like TEAMChem not only provide excipients like TEG but also offer consulting on the complex interplay between excipients and APIs, optimizing formulation processes.
Triethylene Glycol as a Versatile Solvent in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing

Beyond its presence in the final medication, TEG's solvent properties offer significant advantages during the pharmaceutical manufacturing process:
API Extraction and Isolation: TEG can be used to extract specific active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from natural sources like plants or biological materials. This ability aids in the initial isolation of potential drug candidates.
Purification of Intermediates: During the multi-step synthesis of APIs, TEG's solubility properties make it useful in purifying intermediate compounds, ensuring a high-quality final product.
Process Solvent: In various manufacturing stages, TEG can act as a solvent for reactions, cleaning solutions, or as a carrier for other ingredients when water is unsuitable.
Heat Transfer Medium: TEG's thermal properties make it suitable for use in industrial heating and cooling systems, helping to maintain optimal temperatures for precise pharmaceutical production processes.
Safety Considerations: Triethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Applications
While TEG offers significant benefits in pharmaceutical development, its safe and responsible use is essential. Key safety considerations include:
Regulatory Oversight: Regulatory bodies like the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency) establish strict guidelines for TEG's use in specific pharmaceutical applications, covering aspects like concentration limits, acceptable exposure levels, and dosage restrictions.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Pharmaceutical manufacturers must strictly adhere to GMP standards. This ensures the TEG used is of high purity and that appropriate quality control measures are in place during all stages of production.
Potential Concerns: High doses or prolonged exposure to TEG can have adverse health effects. It's crucial to always adhere to recommended dosages or usage instructions in medications containing TEG.
Patient-specific Considerations: Certain individuals, such as those with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions, may be more sensitive to TEG. Healthcare providers should consider these factors when prescribing medications containing TEG.
Exploring the Compatibility of Triethylene Glycol with Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Ensuring the compatibility between TEG and the chosen active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is a crucial step in pharmaceutical development. Here's why compatibility matters and how it's assessed:
Stability: Incompatible combinations of TEG and APIs can lead to drug degradation, reduced potency, or changes in the medication's physical properties over time.
Efficacy: TEG's interactions with an API could potentially affect the drug's ability to dissolve, how it's absorbed by the body, and ultimately, its effectiveness in treating the intended condition.
Safety: In rare cases, incompatibilities might lead to the formation of unwanted byproducts or changes in toxicity, posing potential safety risks.
How Compatibility is Assessed
Pre-formulation Studies: Before large-scale production, compatibility studies are conducted using various techniques, including:
Chemical analysis to examine potential interactions on a molecular level.
Physical stability tests to observe changes in appearance, precipitation, or other signs of degradation.
Performance testing to evaluate how the combination impacts drug release, dissolution, and other key properties.
Future Perspectives: Triethylene Glycol's Role in Advancing Pharmaceutical Technologies
TEG's versatility and unique properties position it to play an evolving role in shaping the future of medicine. Here are some exciting areas where TEG's influence is likely to grow:
Personalized Medicine: TEG's role in tailored drug delivery systems could pave the way for medications customized to individual patient needs, potentially improving treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects.
Targeted Drug Delivery: TEG's integration into advanced drug carriers like nanoparticles and liposomes could enable the precise delivery of medications directly to diseased cells or tissues, maximizing efficacy and reducing unwanted side effects.
Biocompatible Materials: TEG may be explored for the development of biocompatible coatings for medical implants and devices, improving their integration within the body and reducing adverse reactions.
Tissue Engineering: TEG's potential role in formulations for cell culture and tissue regeneration could contribute to significant advancements in the field of regenerative medicine.
Green Pharmaceuticals: Research may explore how TEG can contribute to more sustainable and environmentally friendly drug manufacturing processes.
Driving Innovation: TEAMChem actively collaborates with pharmaceutical companies, exploring new applications for TEG and its derivatives to support cutting-edge drug development.
Innovative Uses of Triethylene Glycol in Novel Drug Development

Beyond its traditional roles, TEG is finding innovative applications in cutting-edge drug development strategies:
Drug Carrier Integration: TEG can be incorporated into the design of novel drug carriers like liposomes, micelles, and nanoparticles. This enhances their stability, biocompatibility, and ability to deliver drugs effectively to target sites.
Controlled Release Formulations: TEG can be a component in formulations that provide sustained or modified drug release patterns. This improves drug delivery over time, potentially reducing dosing frequency for patients.
Solubility Enhancement for Challenging APIs: For new drug candidates with poor solubility, TEG can be a vital tool in developing formulations that enable their therapeutic potential.
Biocompatibility Enhancement: TEG's use in coatings or surface modifications of medical devices and implants can help minimize adverse reactions and improve acceptance by the body.
Triethylene Glycol Derivatives: Potential Applications in Pharmaceuticals
TEG serves as a valuable precursor in the synthesis of various derivatives, opening up new possibilities within the pharmaceutical landscape:
Polyethylene Glycols (PEGs): PEGs of varying molecular weights find diverse applications. They can act as solubilizers, excipients, viscosity modifiers, and even form the basis of drug conjugation techniques (known as PEGylation) to improve drug delivery and reduce side effects.
Esters of TEG: Exploration of TEG esters could yield potential prodrugs (allowing modified drug release), permeation enhancers (improving drug absorption through the skin or other barriers), or find uses as pharmaceutical solvents with tailored properties.
Other Potential Derivatives: Research into TEG derivatives could uncover new compounds with unique pharmaceutical applications related to drug delivery optimization, tissue targeting, or biocompatibility enhancement.
TEG: A Multifaceted Solution
This article attempts to establish that Triethylene Glycol is a remarkably versatile compound with applications in drug formulation, manufacturing processes, and the development of innovative drug delivery systems. The next step is to partner with companies like TEAMChem which provide not only the essential supply of TEG but also offer technical support to maximize its potential. Ongoing research promises new breakthroughs in drug delivery and pharmaceutical technology.
Let's Discuss Your TEG Needs – Contact Team Chemicals Today
If you have questions about TEG's applications or are interested in exploring how TEAMChem can support your pharmaceutical projects, don't hesitate to reach out!